
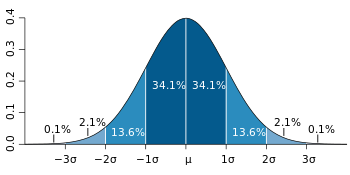
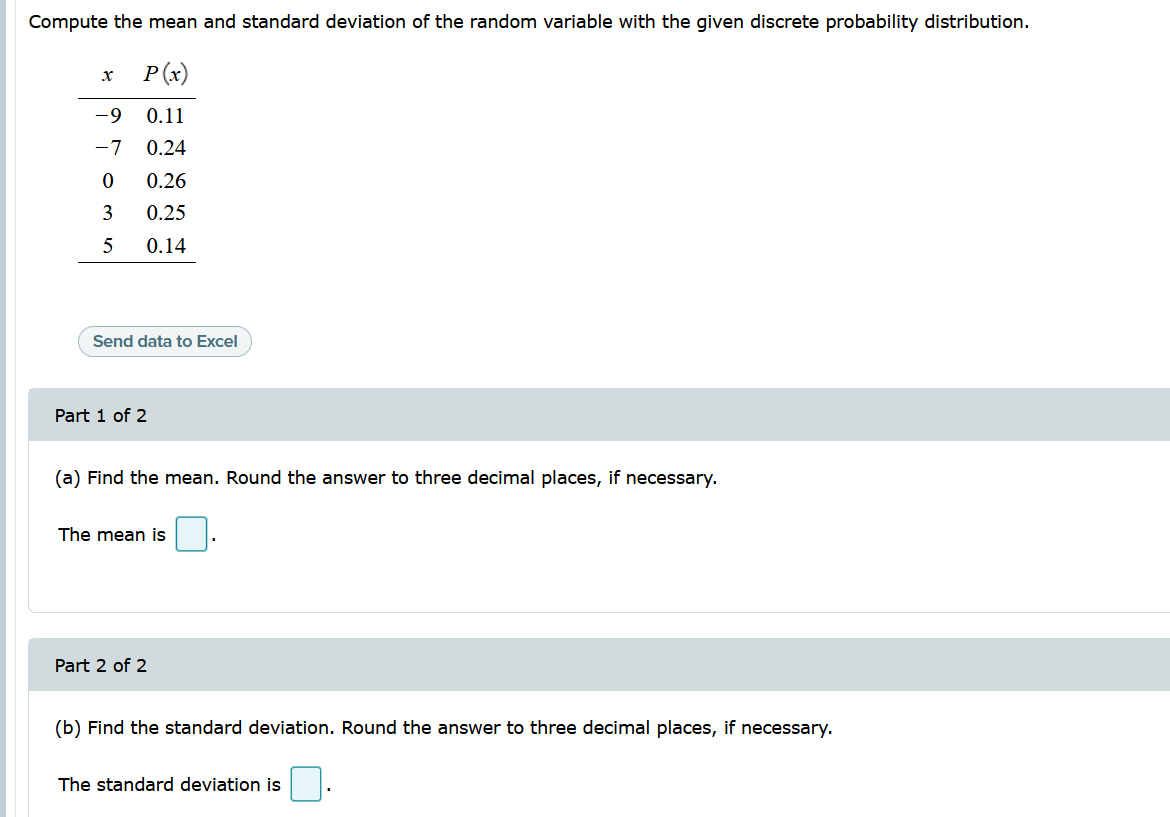
Population Variance (used when the population is known) Larger Variance means the data are more spread out.
/NORM-56cc4e475f9b5879cc58d3d5.jpg)
There are two kinds of Variance – Sample Variance and Population Variance. Variance is defined as the average of the squared differences from the Mean. Suppose data set 1, 3, 5, 7 lie in Range A1:A4. To calculate Interquartile Range in Excel, use either PERCENTILE.EXC or PERCENTILE.INC Function to separately calculate P25 and P 75, and then find the difference.
#PROBABILITY GIVEN MEAN AND STANDARD DEVIATION EXCEL HOW TO#
To understand how to calculate percentile, click here to read my previous post. Interquartile RangeĪnother type of Range called Interquartile Range (IQR) which measures the difference between 75th and 25th observation using the below formula. Range only reflects the difference between largest and smallest observation, but it fails to reflect how data is centralized. Range = largest observation - smallest observation Range is the easiest way to describe dispersion using the below formula. Variability is also known as dispersion, it is to measure of how data are spread out.įor example, data set 100, 130, 160 is less spread out than data set 1, 50, 100, 150, 200 In this tutorial, I will explain how to measure variability using Range, Variance, Standard Deviation. In the previous post, I have explained how to measure the central tendency using Mean, Mode, Median. Where $Z\sim N\left(0,1\right)$ is the standard normal distribution.This Excel tutorial explains how to measure variability using Range, Variance, Standard Deviation.Įxcel calculate Covariance, Coefficient of Correlation Excel Range, Variance, Standard Deviation So what is the distribution of the combined weight of the five bags? That is, what distribution does $\sum_\right)\\ Let's refer to the weight of these five randomly chosen bags as $X_i$, $i=1,\ldots,5$. This question assumes that the weight of each bag independently follows a normal distribution with mean $\mu=1000g$ and standard deviation $\sigma=10g$.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
